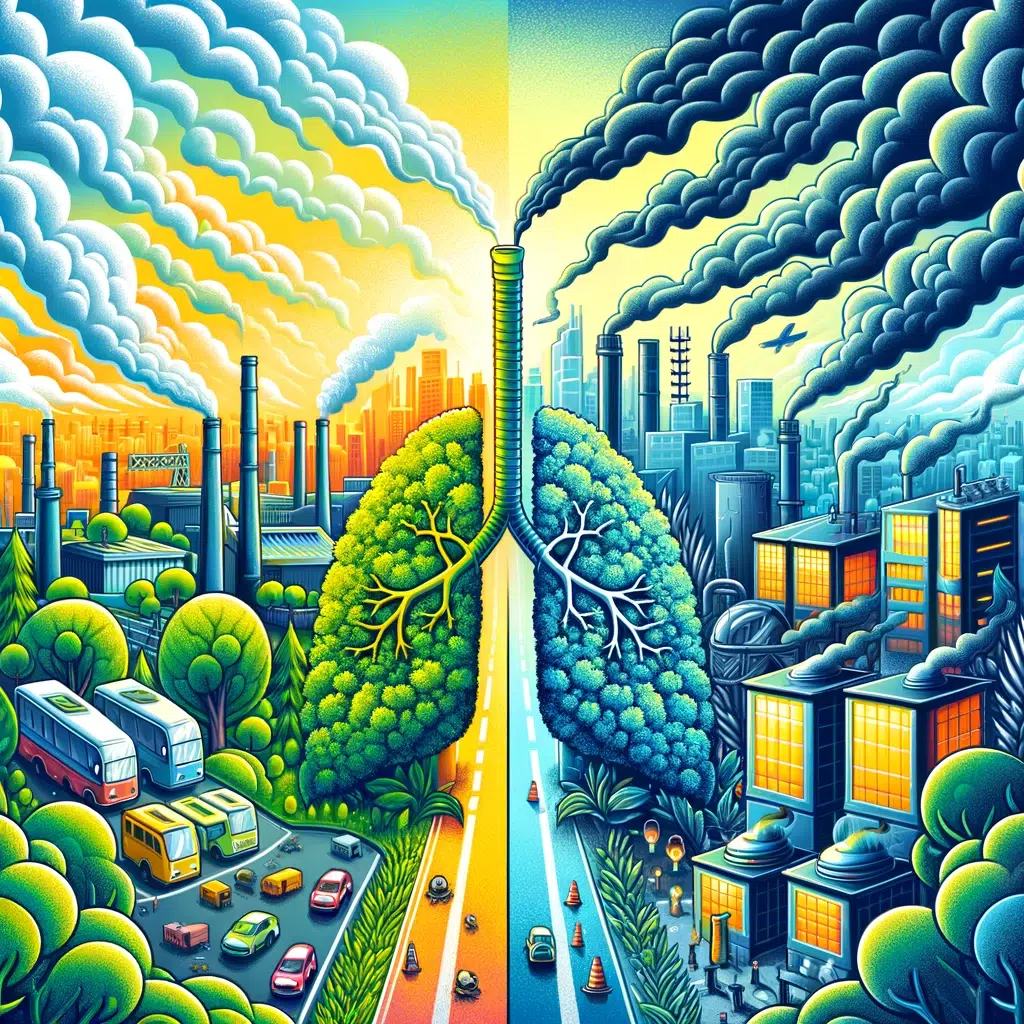
Breathe Easy: Navigating the Complex World of Air Pollution
Air pollution, a pervasive challenge in our modern world, impacts everything from our health to the environment. This comprehensive guide delves into the various facets of air pollution, offering insights and solutions for a cleaner future.
Introduction to Air Pollution
What is Air Pollution?
Air pollution refers to the presence of harmful substances in the atmosphere. It’s a blend of particles and gases that can reach harmful concentrations both outside and indoors. Its impact on human health and the environment has made it a pressing issue for global communities.
Brief History and Evolution
The history of air pollution dates back to ancient times, but it became a significant concern during the Industrial Revolution. Since then, the growth of industries, urbanization, and increased use of fossil fuels have exponentially escalated the problem.
Understanding the Causes
Natural vs. Man-made Sources
While natural events like volcanic eruptions contribute to air pollution, human activities are the primary culprits. This includes industrial processes, vehicle emissions, and deforestation.
Industrial Contributions
Industries, especially those reliant on fossil fuels, are major contributors to air pollution. They release a variety of pollutants, including particulate matter and toxic gases.
Vehicle Emissions and Urbanization
The growth of cities and the reliance on vehicles for transportation have significantly increased air pollution levels. Cars, trucks, and buses emit carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and other pollutants that deteriorate air quality.
Agricultural Activities
Farming practices, including livestock production and the use of fertilizers, release methane and ammonia, contributing significantly to air pollution.
Types of Air Pollutants
Particulate Matter and Its Variants
Particulate matter (PM), especially PM2.5 and PM10, are tiny particles that pose significant health risks. They can penetrate deep into the lungs and even enter the bloodstream.
Gases: CO2, NOx, SOx, and Ozone
Gases like carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx), and ozone (O3) are key air pollutants. They contribute to the greenhouse effect, acid rain, and respiratory problems.
Organic Compounds and Heavy Metals
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and heavy metals like lead and mercury are also significant air pollutants. They come from various sources, including industrial processes and vehicle emissions.
Global Impact and Scale
Air Pollution Around the World
Air pollution is a global issue, affecting both developed and developing countries. While the severity and types of pollution vary, no region is completely immune to its effects.
Comparing Urban and Rural Scenarios
Urban areas tend to have higher levels of air pollution due to dense populations and more vehicles. However, rural areas are not immune, especially those near industrial or agricultural activities.
Health Effects of Air Pollution
Short-term Health Risks
Short-term exposure to air pollutants can cause respiratory issues, eye irritation, and fatigue. It’s particularly concerning for people with pre-existing health conditions.
Long-term Health Consequences
Long-term exposure can lead to chronic respiratory diseases, heart disease, lung cancer, and even early death. Children, the elderly, and those with health conditions are particularly vulnerable.
Vulnerable Populations
Certain populations are more susceptible to the effects of air pollution. This includes young children, the elderly, and people with chronic health conditions.
Environmental Consequences
Effect on Wildlife and Biodiversity
Air pollution doesn’t just affect humans; it also has a profound impact on wildlife and biodiversity. Pollutants can harm ecosystems, affect plant growth, and disrupt animal habitats.
Climate Change Connections
Air pollutants like carbon dioxide and methane are significant contributors to climate change. They trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to global warming and its associated effects.
Acid Rain and Water Pollution
Air pollutants can lead to acid rain, which damages forests, harms aquatic life, and corrodes buildings. They also contribute to water pollution when they settle into water bodies.
Technological Solutions
Innovations in Emission Control
Advancements in technology have led to more efficient ways to control emissions from industries and vehicles. This includes scrubbers, filters, and cleaner fuel technologies.
Renewable Energy and Air Quality
The shift towards renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power significantly reduces air pollution. These sources emit little to no pollutants compared to fossil fuels.
Smart Cities and Sustainable Urban Planning
The concept of smart cities, which integrate technology, urban planning, and sustainability, can play a crucial role in reducing air pollution. This includes green spaces, sustainable transportation, and energy-efficient buildings.
Legislation and Policy
Global Agreements and Protocols
International agreements like the Paris Agreement aim to reduce air pollution and mitigate its impact on climate change. These agreements set targets for reducing emissions and promote sustainable practices.
National Policies and Enforcement
Countries have implemented various policies to combat air pollution. This includes emission standards for vehicles, regulations for industries, and incentives for clean energy.
Local Initiatives and Community Actions
Local governments and communities also play a crucial role. Initiatives like car-free days, tree planting, and public awareness campaigns can make a significant difference.
Public Awareness and Education
Role of Media and Campaigns
Media campaigns and educational programs are essential for raising awareness about air pollution. They help inform the public about the causes, effects, and ways to reduce pollution.
Educational Initiatives for All Ages
Schools and educational institutions can integrate air pollution and environmental studies into their curricula. This helps inculcate awareness and responsibility from a young age.
Personal Responsibility and Action
Reducing Personal Carbon Footprint
Individuals can contribute by reducing their carbon footprint. This includes using public transportation, carpooling, and adopting energy-efficient practices at home.
Sustainable Lifestyle Choices
Making sustainable choices in daily life, like using eco-friendly products, reducing waste, and conserving energy, can collectively make a significant impact.
Future Perspectives
Emerging Trends and Research
Ongoing research and emerging trends are continuously shaping our understanding and approach to air pollution. Innovations in clean energy and sustainable practices are at the forefront of this change.
Predictions and Projections
Experts predict that with collective efforts and technological advancements, it’s possible to significantly reduce air pollution. However, this requires global cooperation and sustained commitment.
Air Pollution FAQs
- How does air pollution affect human health? Air pollution can cause a range of health issues, from respiratory problems to chronic diseases like heart conditions and cancer.
- What are the main sources of air pollution? The primary sources include industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, agricultural activities, and burning of fossil fuels.
- Can air pollution be reduced? Yes, through a combination of policy changes, technological innovations, and individual actions, air pollution levels can be reduced.
- What role do individuals play in reducing air pollution? Individuals can contribute by adopting sustainable practices, reducing vehicle usage, and supporting clean energy initiatives.
- How does air pollution impact climate change? Air pollutants like greenhouse gases contribute to global warming, which is a major aspect of climate change.
- What are the most effective ways to combat air pollution? Effective methods include improving industrial and vehicle emissions standards, transitioning to renewable energy, and increasing public awareness and education.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tackling air pollution requires a multi-faceted approach involving global cooperation, innovative technologies, proactive policies, and individual responsibility. By understanding its causes, effects, and solutions, we can work towards a healthier planet and a sustainable future.